Need reliable information on Pfizer Viagra? Focus on its active ingredient, sildenafil citrate. This is key to understanding its effects and potential side effects. Knowing this helps you make informed decisions about your health.
Sildenafil citrate works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection. However, it’s crucial to consult a doctor before use. Your physician can assess your health status and determine if Viagra is appropriate and safe for you, considering any pre-existing conditions or medications you’re currently taking.
Potential side effects include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion. These are often mild and temporary. Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. Always read the patient information leaflet provided with your prescription for a complete overview of potential risks and benefits.
Remember: Viagra is a prescription medication. Never obtain it from unauthorized sources. Counterfeit Viagra can contain dangerous ingredients. Your health is paramount. Obtain your prescription from a reputable pharmacy or healthcare provider. They can guide you towards the safest and most effective treatment options for your individual needs.
- Pfizer Viagra: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
- Increased Blood Flow & Erection
- Important Considerations
- Viagra Dosage and Administration: A Practical Guide
- Adjusting Your Dosage
- Administration Guidelines
- Important Considerations
- Possible Side Effects
- Common Side Effects and Potential Risks of Viagra
- Cardiovascular Risks
- Drug Interactions
- Rare but Serious Side Effects
- Recommendations
- Contraindications
- Viagra and Other Medications: Potential Interactions
- Medication Groups Requiring Caution
- Specific Examples of Interactions
- Next Steps
- Who Should Not Take Viagra? Contraindications and Precautions
- Viagra vs. Alternatives: Comparing Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
- Finding Genuine Viagra: Avoiding Counterfeit Medications
- Verifying Your Pharmacy
- Inspecting the Packaging
Pfizer Viagra: A Detailed Overview
Pfizer Viagra, containing sildenafil citrate, is a prescription medication for erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
Dosage typically starts at 50mg, taken as needed, one hour before sexual activity. Your doctor might adjust this based on your response and overall health. Never exceed the recommended dosage.
Common side effects include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. More serious, though rare, side effects include vision changes and prolonged erection (priapism). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with heart conditions, low blood pressure, or certain eye problems should discuss its use with their physician. It also interacts with some medications, notably nitrates. Always provide your doctor with a complete medical history.
Viagra’s effectiveness varies. Factors like age, overall health, and the underlying cause of ED can influence its efficacy. Open communication with your doctor is key to maximizing treatment success.
While Viagra is a highly effective treatment option for many men, it’s crucial to remember it’s a medication requiring a doctor’s prescription. Consult a healthcare professional to determine if Viagra is right for you and to discuss potential risks and benefits.
Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This enzyme breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule for achieving and maintaining an erection. By blocking PDE5, Viagra increases cGMP levels. Higher cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, increasing blood flow.
Increased Blood Flow & Erection
This increased blood flow engorges the penis’s erectile tissue, leading to an erection. The effect is triggered by sexual stimulation; Viagra doesn’t cause erections spontaneously. It enhances the body’s natural response to sexual stimulation. The duration of action varies, typically lasting several hours. Individual responses may differ.
Important Considerations
Viagra’s effectiveness depends on various factors, including overall health and the presence of other medical conditions. Consult a doctor before using Viagra, especially if you have heart problems, high blood pressure, or take other medications. They can assess your suitability and potential side effects.
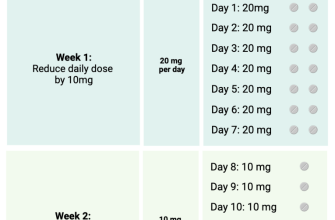
Viagra Dosage and Administration: A Practical Guide
Start with the recommended dose of 50 mg taken orally about an hour before sexual activity.
Adjusting Your Dosage
Your doctor might adjust this based on your response and individual needs. Possible adjustments range from 25 mg (minimum dose) to 100 mg (maximum dose) per day. Don’t exceed the maximum dose.
- Less effective? Your doctor might suggest increasing the dose, but only within the safe limits.
- Side effects? If you experience unwanted side effects, your doctor may lower the dosage.
Dosage adjustments are always best discussed with your physician.
Administration Guidelines
- Take Viagra with a glass of water.
- Avoid taking it with high-fat meals, as this can delay absorption.
- The medication is usually effective for 4-5 hours.
- Don’t take it more than once a day.
- Consult your doctor before combining it with other medications, especially nitrates.
Important Considerations
Possible Side Effects
- Headache
- Facial flushing
- Indigestion
- Nasal congestion
- Visual disturbances
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects, seek immediate medical attention.
This information is for guidance only. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and read the patient information leaflet provided with your prescription.
Common Side Effects and Potential Risks of Viagra
Viagra, like all medications, carries potential side effects. The most common include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. These are usually mild and temporary. More serious, though less frequent, side effects include vision changes (blurred vision, blue tint to vision), hearing loss, and prolonged erection (priapism). If you experience a prolonged erection lasting more than four hours, seek immediate medical attention. This is a medical emergency.
Cardiovascular Risks
Viagra can affect blood pressure. Men with pre-existing heart conditions should discuss the risks with their doctor before using Viagra. Chest pain or shortness of breath during sexual activity requires immediate medical attention. This could signal a serious heart problem.
Drug Interactions
Certain medications interact negatively with Viagra. Nitrate medications, commonly prescribed for heart conditions, are a significant concern. Combining them can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Always inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Viagra. This will help ensure your safety.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Rarely, Viagra can cause more serious side effects such as stroke, heart attack, and sudden death. While the risk is low, it’s important to be aware of these possibilities. Regular monitoring of your overall health while using Viagra is recommended.
Recommendations
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Discuss any concerns or side effects you experience with your healthcare provider. They can assess your individual risk factors and adjust your treatment accordingly. Don’t hesitate to ask questions; open communication with your doctor is paramount.
Contraindications
Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Men with certain medical conditions, such as severe heart or liver disease, should not use it. Your doctor will determine if Viagra is appropriate for you based on your health history.
Viagra and Other Medications: Potential Interactions
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Viagra. This includes nitroglycerin or other nitrates used for chest pain; combining them with Viagra can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
Medication Groups Requiring Caution
Alpha-blockers: These medications, often prescribed for high blood pressure or prostate problems, can interact with Viagra, potentially leading to dizziness or fainting. Your doctor may adjust your dosages or suggest alternative treatments.
Blood thinners: While not a direct interaction, Viagra can slightly increase bleeding risk. Discuss this with your doctor, especially if you’re already on anticoagulants.
CYP3A4 inhibitors: Certain medications, like antifungal drugs like ketoconazole and some antibiotics, inhibit the enzyme that breaks down Viagra. This can increase Viagra’s effects and potentially lead to side effects. Your doctor might adjust your Viagra dose or suggest a different medication.
Specific Examples of Interactions
Specific interactions vary widely. This is not an exhaustive list. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for detailed information regarding potential interactions.
Ritonavir (Norvir): A protease inhibitor used for HIV, significantly increases Viagra’s concentration in the blood, requiring careful monitoring and potential dose reduction.
Erythromycin: An antibiotic that, like some others, can affect Viagra’s metabolism and increase its side effects.
Grapefruit juice: Although not a medication, grapefruit juice inhibits the same enzyme as some drugs, increasing Viagra’s levels. Avoid grapefruit while using Viagra.
Next Steps
Transparency is key. Open communication with your doctor about your medical history and all medications ensures safe and effective treatment. Never self-medicate or alter dosages without consulting a healthcare professional. They can help manage potential risks and maximize the benefits of your treatment plan.
Who Should Not Take Viagra? Contraindications and Precautions
Viagra, or sildenafil, is not suitable for everyone. Certain medical conditions and medications can interact negatively with it. Always consult your doctor before taking Viagra.
Here are some key contraindications:
- Heart problems: Viagra can lower blood pressure, posing risks for those with angina, heart failure, or recently experienced heart attack or stroke.
- Low blood pressure: Viagra’s blood pressure-lowering effect can be dangerous for individuals already experiencing hypotension.
- Liver or kidney disease: These conditions can impair Viagra’s metabolism and elimination from the body, potentially leading to adverse effects.
- Retinitis pigmentosa: This rare eye disease can worsen with Viagra use.
- Blood cell disorders: Viagra may increase the risk of bleeding in individuals with conditions like sickle cell anemia or leukemia.
- Recent eye problems: Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a risk factor; avoid Viagra if you’ve experienced this.
- Deformities of the penis: Conditions like Peyronie’s disease should be discussed with a doctor before Viagra use.
Specific medication interactions are also important:
- Nitrates: Combining Viagra with nitrates (used for chest pain) can cause dangerously low blood pressure.
- Alpha-blockers: Concurrent use can also significantly lower blood pressure.
- Some HIV protease inhibitors: Interaction is possible; discuss with your doctor.
- Certain antifungals: Check for potential interactions with your doctor.
Precautions:
- Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking.
- Discuss any pre-existing health conditions.
- Follow the prescribed dosage carefully.
- Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, dizziness, or vision changes.
- Viagra is not a recreational drug and should only be taken as directed.
This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication, including Viagra.
Viagra vs. Alternatives: Comparing Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
Choosing the right erectile dysfunction (ED) treatment depends on individual needs and preferences. Viagra (sildenafil) is a popular choice, working by increasing blood flow to the penis. However, several alternatives exist, each with its own mechanism and potential side effects.
| Treatment | Mechanism | Side Effects | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viagra (Sildenafil) | Increases blood flow to the penis | Headache, flushing, nasal congestion | Not suitable for everyone, particularly those with heart conditions. Requires sexual stimulation. |
| Cialis (Tadalafil) | Similar to Viagra, but longer-lasting effects | Similar to Viagra, but potentially less frequent | Longer duration may be beneficial for some, but also increases risk of side effects over longer periods. |
| Levitra (Vardenafil) | Similar mechanism to Viagra and Cialis | Similar side effects to Viagra and Cialis | May be preferred by individuals sensitive to specific side effects of Viagra or Cialis. |
| Avanafil (Stendra) | Similar mechanism to Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra | Similar side effects to Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra; faster onset | Faster onset of action may be advantageous for some patients. |
| Alprostadil (Caverject, MUSE) | Directly relaxes penile muscles | Pain, swelling, bruising at injection site (Caverject); urethral irritation (MUSE) | Injected or inserted into the urethra; suitable for patients who cannot tolerate oral medications. |
| Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) | Increases testosterone levels | Increased blood cell production, mood changes | For men with low testosterone levels contributing to ED. Requires blood test to confirm low levels. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Improve overall health and blood flow | Minimal side effects; requires commitment | Diet, exercise, stress management, weight loss may improve ED symptoms naturally. |
This table provides a concise comparison. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any ED treatment to determine the safest and most effective option for your individual circumstances and to discuss potential interactions with other medications you might be taking.
Finding Genuine Viagra: Avoiding Counterfeit Medications
Buy Viagra only from licensed pharmacies. Check for verification seals and authenticity codes on the packaging. These codes allow you to confirm the drug’s legitimacy directly with the manufacturer.
Verifying Your Pharmacy
Always verify the pharmacy’s license and legitimacy before making a purchase. Look for a physical address and contact information readily available on their website. Be wary of pharmacies lacking transparency or operating exclusively online without a clear physical presence. Reputable pharmacies will clearly display licensing details and accreditation.
Inspecting the Packaging
Examine the packaging carefully. Look for inconsistencies in printing, spelling errors, or blurry images. Genuine Viagra packaging is crisp, clear, and consistent with Pfizer’s official branding. Compare the packaging to images found on Pfizer’s official website for a quick verification. Report suspicious websites or products to regulatory authorities like the FDA.
Never buy Viagra from unofficial online marketplaces or individuals offering suspiciously low prices. These are often major red flags indicating counterfeit products. Prioritize your health; purchasing from trusted sources is paramount.